What is Laser Engraving
Introduction
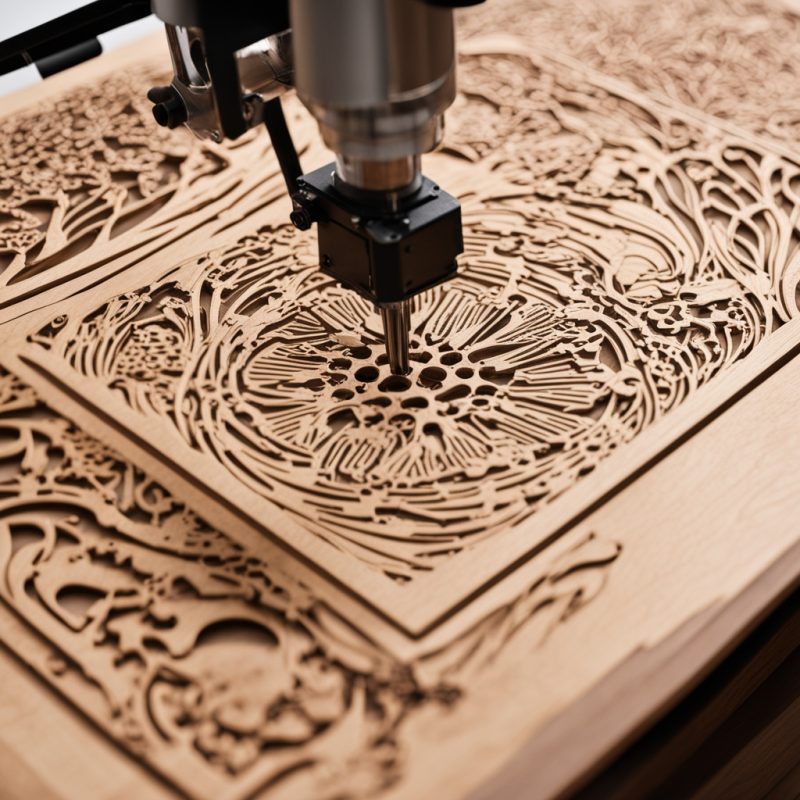
Laser engraving is a sophisticated technology that utilizes high-energy laser beams to create precise and intricate designs on various materials. This process involves focusing a laser beam onto the surface of a material, causing it to vaporize or change color, thus leaving a lasting mark. From personalizing gifts to manufacturing prototypes, laser engraving machines have revolutionized numerous industries. This article delves into the technology behind laser engraving, its applications, machine specifications, material compatibility, safety considerations, industry best practices, cost-benefit analysis, maintenance tips, and exciting project ideas.
Laser Engraving Technology and Applications
Laser engraving technology employs a high-intensity laser beam to precisely remove material from a surface or alter its properties. This non-contact process allows for extreme precision and can produce intricate details and crisp edges. The versatility of laser engraving makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Personalization: Engraving names, dates, and messages on jewelry, gifts, and memorabilia.
- Prototyping: Creating detailed designs and models for product development.
- Art and Craft: Producing intricate artworks, sculptures, and decorative pieces.
- Industrial Marking: Applying serial numbers, barcodes, and logos on products and components.
- Packaging: Enhancing brand identity with custom logos and designs on packaging materials.
The technology can be used on various materials, from metals and plastics to woods and leathers, making it a highly versatile tool for both professional and DIY enthusiasts.
Machine Specifications and Features
Laser engraving machines come in a variety of sizes, power levels, and configurations to cater to different needs. Key specifications and features to consider when choosing a laser engraver include:
- Laser Power: Measured in watts, it determines the speed and depth of engraving. Higher wattage lasers can cut thicker materials and work faster.
- Workspace Dimensions: The size of the engraving bed determines the maximum workpiece dimensions. Larger beds accommodate bigger projects.
- Laser Type: CO2 lasers are commonly used for organic materials like wood and leather, while fiber lasers excel with metals.
- Software Compatibility: Machines should be compatible with industry-standard design software like Adobe Illustrator and AutoCAD for easy file import and editing.
- Automation Features: Advanced models offer features like autofocus, automatic material sensing, and integrated cameras for enhanced precision.
For instance, the what is laser engraving machine from XTool offers a compact design, a powerful diode laser, and a user-friendly interface, making it ideal for beginners and professionals alike.
Material Compatibility
Laser engraving machines can work with a diverse range of materials, each requiring different settings and considerations. Here are some common materials and their compatibility:
- Wood: Easily engraved with detailed patterns. Laser settings can be adjusted to achieve varying depths and textures.
- Leather: Produces clean, precise cuts and engravings. Suitable for personalizing bags, wallets, and accessories.
- Acrylic: Can be cut and engraved, creating vibrant, translucent designs. Care must be taken to avoid melting.
- Metals: Fiber lasers can engrave and mark metals like stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. Material thickness and reflectivity affect processing times.
- Paper and Cardboard: Ideal for creating intricate papercraft and invitations. Fast processing times with clean results.
Understanding material properties and adjusting laser parameters accordingly is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Safety Considerations
Laser engraving machines operate with high-energy beams, making safety a top priority. Here are some essential safety measures:
- Eye Protection: Always wear laser-safe glasses when operating the machine to protect against laser radiation.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation to prevent the accumulation of harmful fumes and particles.
- Fire Prevention: Keep flammable materials away from the laser beam and have fire extinguishers on hand.
- Software Safety Features: Use machines with emergency stop buttons and software that prevents unauthorized operation.
- Training: Operators should receive thorough training on machine operation and safety procedures.
Adhering to these safety guidelines helps prevent accidents and ensures a safe working environment.
Industry Best Practices
Achieving high-quality laser engravings consistently requires following industry best practices:
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate the machine to ensure precision and accuracy.
- Material Preparation: Clean and flatten workpieces to avoid imperfections in the finished product.
- Quality Control: Inspect finished pieces for defects and adjust settings as needed.
- Software Optimization: Utilize software features like vectorization and rasterization to enhance design quality.
Implementing these practices helps maintain consistent quality and maximizes machine efficiency.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Investing in a laser engraving machine can offer significant benefits, but the cost can vary widely depending on machine specifications and features. When considering the purchase, it’s essential to weigh the costs against the potential benefits:
- Initial Investment: High-end machines with advanced features come at a premium price, but they offer greater versatility and efficiency.
- Return on Investment: Evaluate the potential for increased sales, cost savings on outsourcing, and the ability to offer customized services.
- Scalability: Choose a machine that can grow with your business needs, offering expandability in workspace and power.
A well-chosen laser engraver can lead to substantial cost savings and increased profitability over time.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your laser engraver and ensuring optimal performance:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the machine and optics clean to prevent dust accumulation and ensure beam quality.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to reduce wear and tear.
- Alignment Checks: Periodically check and adjust the laser beam alignment to maintain precision.
- Software Updates: Install software updates to access new features and improvements.
- Preventive Maintenance: Schedule routine maintenance checks with a qualified technician.
By adhering to these maintenance tips, you can minimize downtime and maximize the performance of your laser engraver.
Project Ideas and Tutorials
Laser engraving opens up a world of creative possibilities. Here are some inspiring project ideas and tutorials to get you started:
- Personalized Jewelry: Engrave names, initials, or meaningful dates onto rings, bracelets, and pendants.
- Custom Leather Goods: Create personalized wallets, bags, and keychains with intricate designs.
- Wooden Artwork: Produce decorative pieces, coasters, and signs with intricate laser-cut patterns.
- Photo Engraving: Convert photos into grayscale images and engrave them onto wood, leather, or acrylic.
- Holiday Decorations: Design custom ornaments, gifts, and wrapping paper with festive themes.